Key Changes effective from 1st April, 2025

Mandatory Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
The National Informatics Centre (NIC) introduced two-factor authentication (2FA)/multi-factor authentication(MFA) to log in to the e-way bill or e-invoice system a long time ago. This measure required taxpayers to authenticate their login using two or more verification methods, reducing the risk of unauthorised access.
Implementation Timeline:
- January 1, 2025: Mandatory for taxpayers with an Annual Aggregate Turnover (AATO) exceeding ₹20 Crores.
- February 1, 2025: Extended to taxpayers with an AATO exceeding ₹5 Crores.
- April 1, 2025: Applicable to all taxpayers, irrespective of turnover.
Compulsory Input Service Distributor (ISD) Registration
Until now, organisations with multiple GST registrations under a single PAN could either use the Input Service Distributor (ISD) mechanism or adopt a cross-charge approach to distribute common input services like rent, audit fees, and software licenses across different units. Many opted for cross-charge due to its operational simplicity, despite its complexities in ITC distribution and tax reconciliation.
However, from April 1, 2025, ISD registration will become mandatory for such taxpayers. Under this model, businesses must issue ISD invoices and file GSTR-6 returns to distribute Input Tax Credit (ITC) across branches, ensuring better traceability and standardised reporting.
Amendments to GSTR-7 and GSTR-8 Formats
Via notification no. 09/2025–Central Tax, dated February 11, 2025,the government introduced changes to the GSTR-7 (TDS) and GSTR-8 (TCS by e-commerce operators) forms to capture more detailed transaction information.
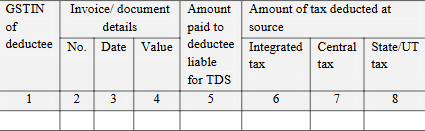
- GSTR-7: The format of GSTR-7 is modified to include invoice/document-wise details of tax deducted, requiring additional data such as the deductee’s GSTIN, invoice details, the amount paid, and tax deducted.
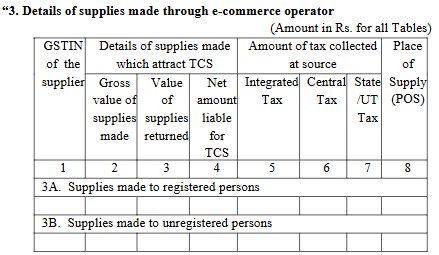
- GSTR-8: Form GSTR-8 was updated to provide comprehensive details of supplies made through e-commerce platforms, facilitating improved compliance and reporting accuracy.
e-Way Bill Generation and Extension Restrictions
New limitations are imposed on the generation and extension of e-Way Bills to enhance the integrity of goods movement tracking:
- Generation Restriction: Effective January 1, 2025, e-Way Bills can only be generated for documents dated within the preceding 180 days. For instance, documents dated before October 3, 2024, will be ineligible for e-Way Bill generation from April 1, 2025.
- Extension Limitation: Extensions of e-Way Bills will be capped at 360 days from the original generation date. An e-Way Bill generated on April 1, 2025, can only be extended until March 27, 2026.
30-Day Time Limit for E-Invoice Reporting Extended to More Taxpayers
The government has steadily tightened e-invoicing timelines to improve reporting discipline and plug tax evasion gaps. As part of this initiative, the 30-day time limit for reporting e-invoices on the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) has now been extended to those with AATO above ₹10 crore, effective April 1, 2025. This was previously applied to businesses with AATO above ₹100 crore. This means that taxpayers in this bracket must ensure that all B2B invoices are reported to the IRP within 30 days from the invoice date. Failure to do so will result in the invoice being rejected for IRN generation, which can impact input credit claims and delay downstream compliance.


